What filters will help remove iron from water?
Content:
The safe amount of iron in water is within the range of 0.1-0.3 mg/l, and in practice its content can be 10 times higher. In this regard, questions arise: how to purify water from iron, is such purification necessary, and how to determine the composition of water?
Iron in water can be in various forms:
- divalent (soluble);
- trivalent (insoluble);
- organic: soluble (polyphosphates), bacterial and insoluble (colloidal).
To choose the right purification system, you need to know not only the level of iron, but also its shape.

How to determine the concentration of iron in water?
In conditions of centralized water supply in the city, the reason for the increase in iron is always steel water pipes. Simply put, rust from the pipeline mixes with water, but does not dissolve. The easiest way to determine the presence of rust (ferric iron) is to let the water sit in any transparent container. If after a few hours a reddish sediment forms at the bottom, it’s time to take safety measures and purify the water of ferric iron.
Advice
A rusty coating on the sink, bathtub or toilet is a clear indication that rust from the pipes is getting into your faucet.With such “symptoms,” you need to move from diagnosis to eliminating the problem.
From artesian wells, water with iron (ferrous) dissolved in it enters the house. An increase in its level can be determined visually - the water becomes slightly yellowish. But the color change does not always occur. In this case, a weak solution of potassium permanganate will help. If the pink solution is added to water with a high iron content, its color will change to yellowish-brown.
Colloidal iron may be present if the collection is from a shallow well that receives surface water. In this case, the settled water will be cloudy; the suspension of such iron molecules will not settle to the bottom. If a film forms on the surface of the water, there are iron bacteria in the water.
If the water from the tap has the characteristics listed above or a metallic taste, you need to select a purification system. To do this with maximum efficiency, you need to take a water sample to the laboratory. Having the research results in hand, you can choose the right iron removal system.
Cleaning methods
There are two types of methods for removing iron and its compounds from water - reagent and non-reagent. If filters with reagents are used, you need to monitor their replenishment.
Filtering can be done in the following way:
- aeration;
- ion purification;
- membrane, including osmotic cleaning;
- ultrafiltration;
- sediment filtration;
- mechanical cleaning.
It should be noted that there is no universal method for cleaning all types of contaminants. This is why it is so important to determine what type of contamination is present.
Mechanical cleaning
Mechanical filtration systems (mechanical cartridge filters) have proven themselves well. They are suitable if you need to purify water from large fractions of insoluble iron (rust). To remove oxides, propylene cartridges and cartridges with fine-grained granulite are used.
They are mainly used in apartments and houses with a centralized water supply, since it is impossible to purify water from a well using this method. More precisely, mechanical filters are also used in cottages, but with preliminary oxidation (aeration) of metal compounds.
The mechanical purification method with macrofilters (retained particle size is more than 15 microns) is used for water pre-purification. Cartridges with 5 micron cells are installed for fine filtration.
Advice
Pre-filtration or a coarse filter retains large fractions, making fine-mesh cartridges last much longer.
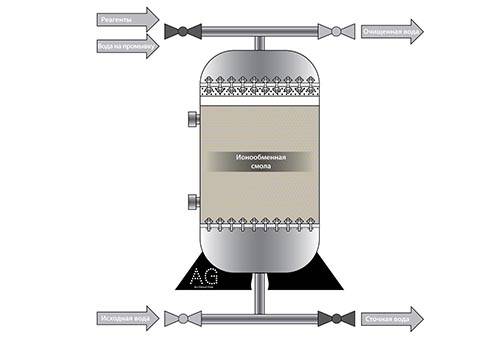
Ionic filtration
Water purification using ion exchange is a reagent method that allows you to selectively change the ionic composition of water. If the task is to remove iron, then catalytic resins with various fractional additives are used as ion exchangers in filters. They replace metal ions with sodium ions.
The reagent medium loses its abilities over time, but can be restored. For this, use citric acid or table salt (solution). The advantage of this method is that deferrization does not entail the precipitation of hardness salts and removes not only rust, but also metals dissolved in water, including manganese. The disadvantages include the fact that catalytic resins are only partially restored under the influence of a salt solution, and after 2-3 years they completely exhaust their resource.
Aeration
Water supplied from an artesian well contains various metal compounds, including divalent iron in a dissolved state. Since it is impossible to purify water from a well without preliminary oxidation of divalent iron, the method of aeration is used, that is, saturating the water with oxygen. As a result, the metal changes from a dissolved state to an insoluble oxide, and after that it can be removed using a mechanical or other filter.
Aeration can be done using both pressure and non-pressure methods.
- With gravity aeration, water is supplied to an oxidation tank, in which atomization and showering occur. Dusting is done using nozzles or an injector. Oxides accumulate at the bottom of the aeration tank, and it must be cleaned periodically - from two to five times a year, depending on the degree of water contamination.
- Pressure aeration is carried out in a static mixer or aeration column. They are a contact chamber into which water is supplied (filled approximately two-thirds), and air is supplied through a tube to the level of the middle of the column/mixer. Thus, bubbling of bubbles of a saturated air mixture occurs and oxidation of divalent iron occurs. In addition, additional (secondary) aeration occurs in the column at the boundary of water and air, increasing the quality of cleaning.
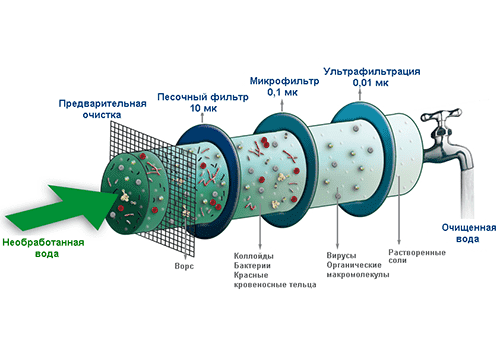
Reverse osmosis
The reverse osmosis purification system is the most advanced fine filter with pre-cleaning. Using reverse osmosis membranes, high-quality filtration of drinking water from all impurities occurs.The pre-filter built into the system retains insoluble metal particles with a fraction of more than 0.5 microns and inorganic iron dissolved in water.
The main stage of cleaning is carried out by a membrane with pores of 0.0001 microns in size, under the influence of a pressure difference. As a result, pure water molecules are separated from high-density water (saturated with organic iron compounds and other pollutants), which is drained into the drainage system. The only disadvantage of a reverse osmosis filter is its low productivity. However, this degree of purification is only needed for drinking water and water for cooking, and reverse osmosis can easily cope with this volume.
Backfill filter with backwash system
Filtration of water with backfill refers to sedimentary and reagent methods. It is necessary for water treatment from wells when the aeration method is not suitable for technical reasons or is insufficient. Branded materials Birm, Manganese Greensand, MTM, Pyrolox are used as a filter medium (backfill). Backfilling reduces the time required for oxidation by hundreds of times.
The automatic cottage deferrizer is designed as follows.
- The filter housing – the cylinder – is filled with filter medium.
- An automatic machine with a timer and flow meter is installed in the upper part of the housing. Its function is to change the direction of water after a specified time during filtration and regeneration.
- Inside the cylinder, a water-lifting pipe passes through the entire backfill layer.
- A flexible tube connects the cylinder to the reagent container.
During the filtration cycle, water passes through the backfill, rises up the water riser pipe and exits the treatment system.When the regeneration cycle begins, water is supplied to the water-lifting tube from above. It loosens the filter bed layer and washes away the iron compounds deposited there. After this, the machine will perform a reagent treatment of the filter medium, which restores its chemical activity.
What to choose?
To choose the right filtration system, as mentioned above, you need to do a water analysis in the laboratory. This will be much cheaper than selecting a filter using trial and error, and will also help install the optimal filtration system. The installation of filters also depends on the purpose for which the water is needed.
Fine filters are unnecessary when it comes to preparing water for domestic (washing, showering) or technical needs. But for drinking water their presence may be mandatory, depending on the results of laboratory tests.





How can you remove iron from water from a well?
At the dacha there is water from an artesian well.I added iodine solution to it, as the article says. the water turned yellow-brown. Looks like it's worth thinking about a filter.