Tablets with vegetables: why is aspirin added to preserves?
Since Soviet times, some housewives have become accustomed to using aspirin in preserving cucumbers and tomatoes. However, doctors say that drugs have no place in homemade pickles and that such canned food can cause serious harm to health. Let's find out how acetylsalicylic acid affects the quality of products and what can replace it when canning.
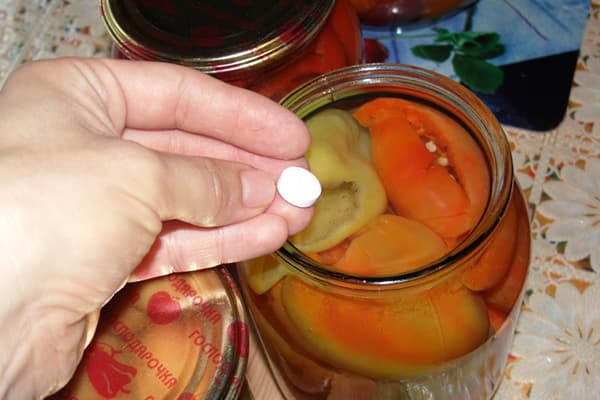

How does aspirin work?
Acetylsalicylic acid, also known as aspirin, is widely used in medicine - it reduces fever, has an analgesic effect, and thins the blood. When dissolved, this substance, like other organic acids, creates an acidic environment. Such an acidic solution is harmful to microorganisms.
Therefore, back in Soviet times, housewives began to add 1-2 antipyretic tablets to jars of cucumbers and tomatoes. Such seams did not spoil for a long time. The availability of the medicine also played a significant role in the popularization of this method: aspirin was very cheap and was in the medicine cabinet in every home.
Despite the high effectiveness of aspirin as a preservative, many doctors have repeatedly expressed the opinion that this substance remains a medicine and its use in cooking is unacceptable due to the health hazard.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has issued a special ban on the use of acetylsalicylic acid in canning.This order made it possible to guarantee the absence of the drug and its derivatives in industrially prepared canned food sold in stores.
Why doesn't medicine have a place in food?
To understand what harm can be caused by preserving tomatoes with aspirin, you need to understand what acetylsalicylic acid is chemically. This substance is a derivative of salicylic acid, which was extracted from willow bark and has been used to treat fever for a long time. Salicylic acid, in turn, is a derivative of a substance toxic to humans - phenol.
Here are the consequences of consuming canned aspirin:
- The medicine (and its breakdown products formed in the brine) is excreted from the body through the kidneys, having a strong destructive effect on them. With frequent use of this substance, pyelonephritis develops - kidney damage.
- The acidic environment of the drug solution and the toxic products of its breakdown have a destructive effect on the stomach and intestines. Acetylsalicylic acid is not recommended for use for peptic ulcers, and even healthy people are advised to take it after meals with milk.
- Chronically taking doses of aspirin with food may lead to an allergy to this drug.
Any of the listed negative effects is a reason to permanently abandon the use of acetylsalicylic acid for canning. This decision is especially relevant these days, when there are many preservatives that do not cause harm to health.
Safe analogues
There are many safe substitutes for aspirin in modern and traditional cooking. The most common option is vinegar.It effectively prevents the development of bacteria in brine, but is not recommended for people with gastritis, stomach ulcers, diabetes, hypertension and many other diseases.
Instead of synthetic acetic acid, it is better to use natural apple cider vinegar. It is rich in potassium and is healthier.
Other substitutes for aspirin can be citric acid, juices of sour fruits and berries (lemon, lingonberries, red currants). These natural preservatives will not harm the body and will ensure good preservation and pleasant taste for canned food.

As I understand, everyone blows their own tune, they write that it is harmful to take aspirin every day.
Doctors advise taking aspirin cardio at night after 50 years to improve heart function...
» Primary prevention of acute myocardial infarction in the presence of risk factors (for example, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, obesity, smoking, old age) and myocardial infarction;
- unstable angina (including suspicion of acute myocardial infarction) and stable angina;
— Prevention of stroke (including in patients with preventive damage to the cerebral circulation);
— Prevention of transient cerebrovascular accident;
— Prevention of thromboembolism after surgery and invasive vascular lesions (for example, coronary artery bypass surgery, carotid endarterectomy, arteriovenous bypass, angioplasty and stenting of the coronary arteries, carotid angioplasty)
— Prevention of venous thrombosis and thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery and its branches (including during prolonged immobilization as a result of extensive surgery).”
My mother-in-law still adds aspirin to her preserves. Maybe after reading the article he will stop doing this.