What needs to be done to prevent potatoes from rotting during storage? Now we'll tell you!
Content:
In winter, you can often find that potatoes are rotting from the inside. Many people don’t know why this happens and what to do to preserve supplies. We suggest you look into the issue. Sometimes it is necessary to take measures against rot immediately, otherwise the entire crop will be lost.

Why do potatoes rot?
To list all the reasons for potato spoilage, there are not enough fingers on your hands. Conventionally, they can be divided into groups:
- infectious diseases;
- varietal characteristics;
- violation of the rules of harvesting, preparation, storage, transportation.
Potatoes often rot from the inside due to several reasons. For example, during transportation the peel is damaged and fungus gets inside. Then, when stored in a warm room with poor ventilation, it multiplies safely. And voila! We cut the tuber, and it’s all rotten inside.
The variety is to blame
Not all potato varieties store well in winter. A striking example of this is early varieties. The skin on the tubers is thin and easily damaged. Therefore, the pulp quickly disappears.
The best keeping quality for late-ripening varieties:
- "Picasso"
- "Nevsky"
- "Nikulinsky"
- "Crane."
The tubers have time to ripen well and become less susceptible to diseases and adverse environmental factors.
Bacteria and fungi are to blame
There are countless potato diseases. Many of them appear during the period of tuber ripening and are initially not visible to the naked eye. “Rot” emerges immediately during storage, after a month or two.
Let's look at the most common infections:
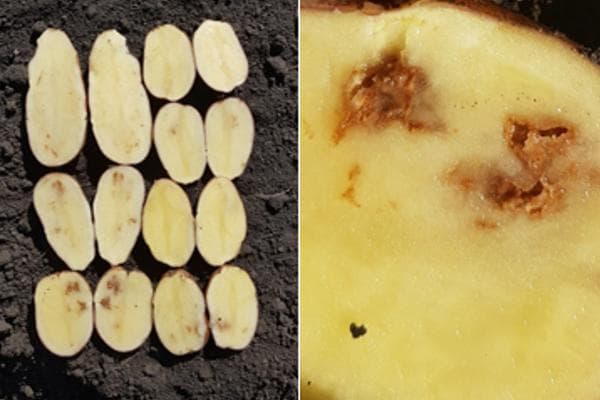
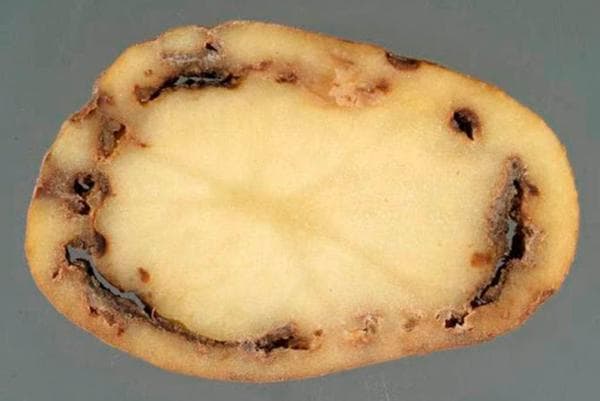
- Ring rot. The bacterial disease is characterized by the appearance of a ring of rot inside the tuber. In this case, the damage is invisible from the outside. The disease develops slowly. It often begins during the growing season. It is transmitted from the mother tuber and through a cutting tool.
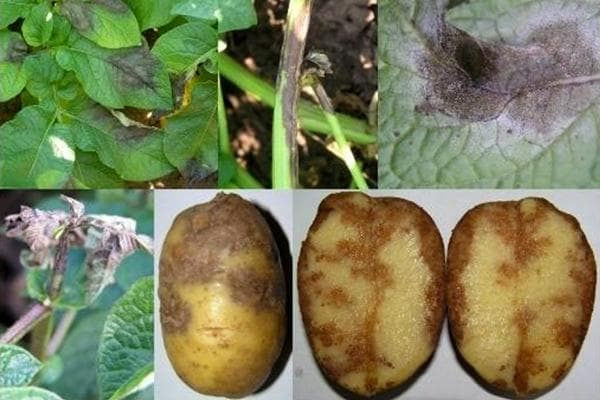
- Late blight. A common fungal disease. Affects the entire plant. Can destroy an entire field in a few weeks. With late blight, dark depressed spots appear on the tubers. If you cut a potato in half, you will find gray-brown sagging inside.
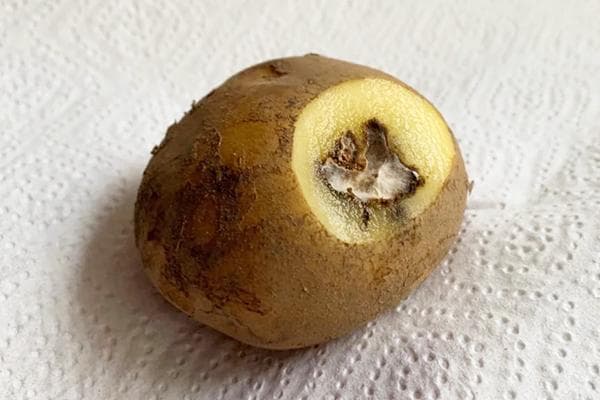
- Dry rot (fusarium). Tubers become infected with fusarium while still in the field. However, the disease manifests itself already during storage. The impetus is a violation of the humidity regime and an increase in temperature. It is transmitted to other tubers when there are cracks in the skin.
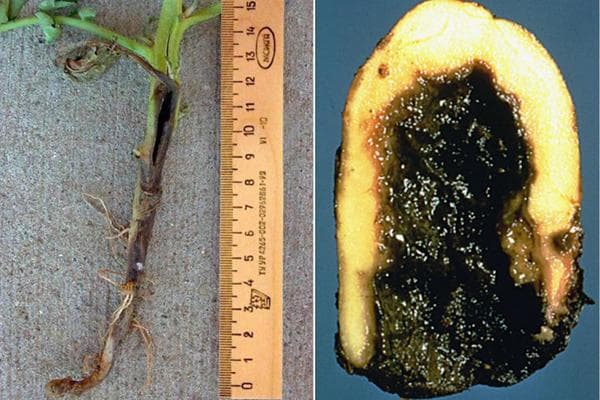
- Blackleg. In rainy years, it destroys up to a third of the entire crop. The bacterial infection penetrates through all kinds of damage and wounds on the plant and tubers. A cavity with soft pulp most often forms inside the potato, which gradually darkens the flesh to black.
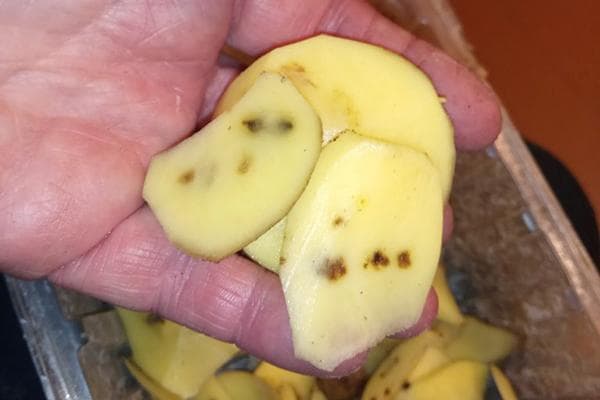
- Potato rustiness (gland spot). The disease develops due to an excess of iron and aluminum salts and a lack of phosphorus during the growing season. It is manifested by the formation of brown spots inside the potatoes.They are dense and have nothing to do with rot. It is not transmitted to healthy tubers.
We have ourselves to blame
If potatoes are stored in a warm or too cold place, you have no one to blame for their spoilage but yourself. Often it rots from the inside due to violation of basic rules:
- storing wet potatoes;
- lack of sorting before storage;
- damage to tubers during transportation;
- unsuitable room: bright, poorly ventilated, too cold or warm;
- unsuitable storage containers (plastic bags, packages).
All these factors accelerate the development of diseases.
A separate point worth highlighting are mistakes made even at the stage of growing a crop:
- Excess nitrogen in the soil causes the potato skins to fail to compact and the cores to remain moist. Such tubers are subject to rapid spoilage.
- Thickened plantings and diseases of the above-ground parts of the plant increase the risk of potatoes rotting from the inside.
- Harvesting in wet weather. It is important to dry wet potatoes well, but this is not always possible.
How to prevent potatoes from rotting?
It is better to combat potato rotting in advance, without waiting for characteristic symptoms to appear.
Preventive measures include:
- Selection of cold potatoes. These are mid- and late-ripening varieties. It is optimal for the potatoes to be dirty (but not excessively) and dry. Washed potatoes look attractive, but are often soggy inside.
- Preparing for storage. It starts with sorting. All damaged and suspicious-looking tubers are removed into a separate bag. They are eaten first. Good potatoes are dried for 2 weeks. To do this, spread it in a thin layer in a well-ventilated area and cover it with burlap.It is optimal to organize a gradual decrease in temperature from +15 to +3 degrees.
- Storage. Potatoes are placed on elevated surfaces (pallets) at a distance of 10–15 cm from the floor and walls. The container must have ventilation holes. The optimal room temperature is +2–3 degrees, humidity is 80–90%. The potatoes should not be exposed to light. The best places for storage are the basement and cellar.
- Removing spoiled and sprouted tubers. Produced as often as possible. At the same time, there is no need to sort through all the stocks. This can cause damage to the skin. It is enough to collect bad potatoes that are in plain sight.
Folk remedies
It is believed that potatoes will be stored better if special products are placed in the boxes.
People have long used the following against potato spoilage:
- beet;
- ash;
- pine branches;
- Rowan casting.
They absorb excess moisture. Thanks to the content of fungicides and other biologically active components, the vital activity of microorganisms slows down. As a result, the potatoes lie well and spoil less.
To reduce the likelihood of potato spoilage, put 2 beets, 1 pine branch, 100 g of rowan leaves in each box. Or pour out a glass of ash.
What to do if the potatoes have already started to spoil?
The defeat of potatoes by rot in the cellar often ends in the complete destruction of stocks. It is possible to save the harvest if measures are taken in a timely manner and the prevalence of the disease is insignificant.
Procedure:
- Cut 1 kg of potatoes in half to assess the extent of the problem. If more than 10% of the reserves are affected, it is unlikely to be saved.
- Carefully sort through the potatoes, removing spoiled tubers.
- Treat the remaining potatoes with a fungicide. For example, "Ditan-45".Dilute 200 g of the drug in 5 liters of water and treat the surface of the tubers. The specified volume of solution is enough for 100 kg of potatoes.
- Dry the tubers.
- Carry out a follow-up test after 2 weeks. If the rot continues to spread, you can repeat the procedure. But, as practice shows, if the first treatment is unsuccessful, the second also ends in failure.
Questions and answers
Do I need to treat potatoes in the basement with preparations for better storage?
To prevent the appearance of rot, the walls of the basement (cellar) and storage containers are treated. Copper sulfate is added to lime and the walls are whitened. All containers are cleaned with a manganese solution. Smoke bombs, which are sold in specialized stores, are also used to disinfect premises.
How to check whether potatoes will rot from the inside during storage?
This is checked as follows: 1 kg of product is tied in a plastic bag and left in a cool, dark place for 2 weeks. A microclimate is formed in the bag, which helps to quickly identify all problematic issues - the presence of “dormant” infections, insufficient preparation of tubers, etc.
To prevent potatoes from rotting during storage, you need to approach their selection and preparation with all responsibility. The choice of storage location and maintaining the required temperature and humidity in the room are of great importance. If, despite all measures, the stocks still begin to rot, fungicide treatment is applied.