Cream or “palm”: how to check the naturalness of the oil?
Very often we complain about the quality of products. The milk is bad, the butter is tasteless... We ourselves are partly to blame for this. The stores also have decent products. You just need to learn how to choose it correctly.
It is very easy to check whether butter is natural. You don’t even need to look at the ingredients to understand which pack is made from vegetable fat. Just feel it. Natural oil is hard, while unnatural oil is soft.
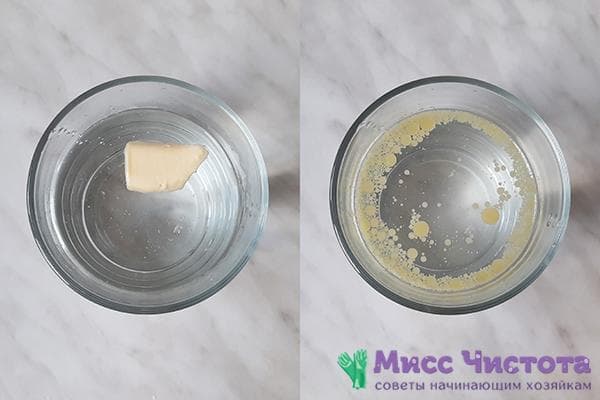

Water solubility test
The melting point of milk fat is lower than that of vegetable fat.
Natural butter quickly dissolves in warm water, breaking up into small droplets of fat. The unnatural floats in warm water in a piece.
To carry out the experiment, pour warm water into a transparent glass. Its temperature should not be higher than body temperature (approximately 37 degrees). Dip a piece of oil inside and after 10 seconds, evaluate the changes that have occurred to it.
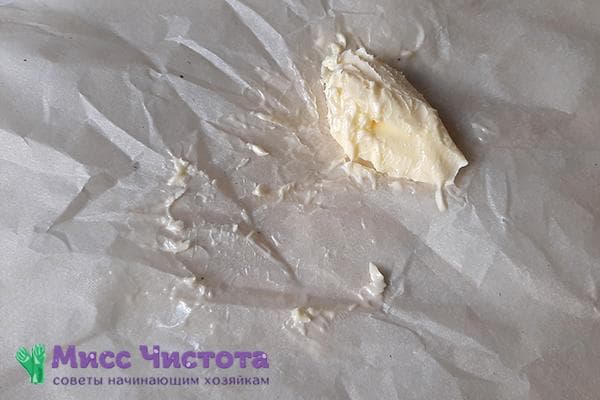
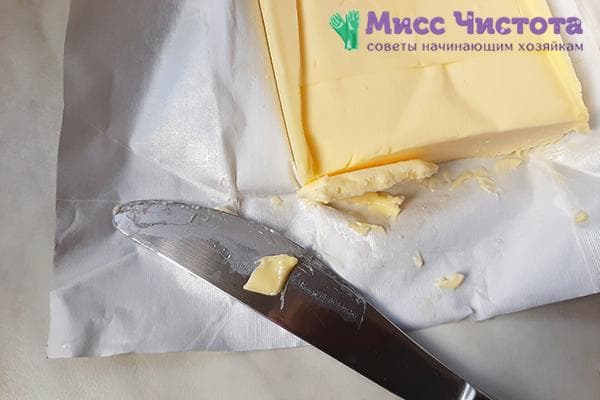
Parchment paper test
In low-quality products, you can notice such a feature as staining. A product containing vegetable fat greatly stains the knife, paper and everything it touches.
Cut a small piece from the butter stick, wrap it in parchment and hold it in your hands. If the paper becomes covered with a sticky layer, it means that this is a fake.
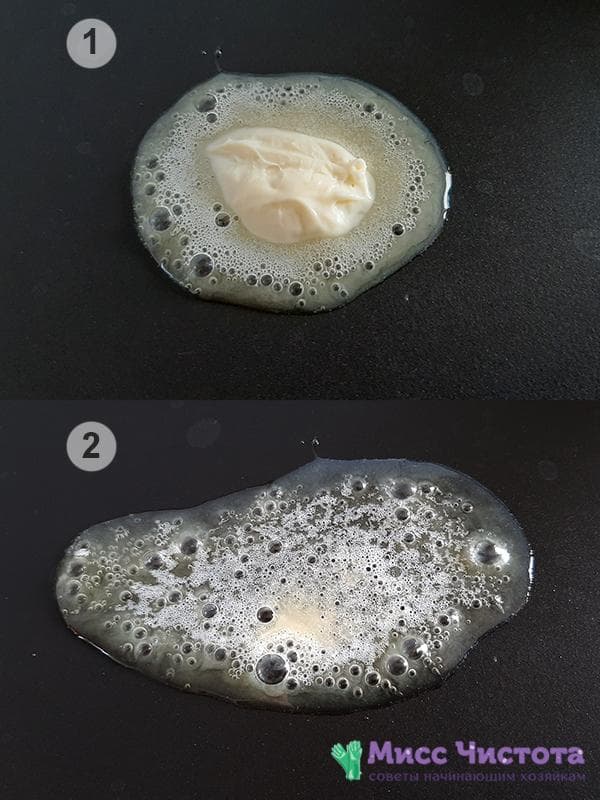
Hot pan test
Real butter melts quickly and silently in a heated frying pan, and also forms a foamy cap. This is how cream manifests itself in the composition.If the product cracks a lot, spreads into a yellowish puddle, and does not form white flakes, then it cannot be called natural.
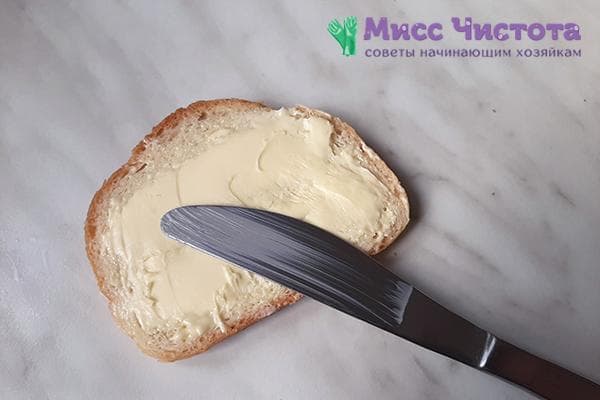
Sandwich test
Place a stick of butter in the freezer for 2 hours. Now take it out and try spreading it on bread. Happened? This means that it is counterfeit based on vegetable fat. It does not freeze to a solid state and remains relatively pliable and soft.
Real butter made with milk and cream is solid. Once you take it out of the freezer, you won't be able to make a sandwich for at least the next 10 minutes. It will crumble, break and every now and then lag behind the bread.
Condensation test
If you conducted a sandwich test, do not rush to hide the product in the refrigerator. Pay attention to the surface of the bar.
Natural oil is dry and clean and does not “sweat” when the temperature changes. The formation of condensation (moisture droplets) is typical for products that are prepared with the addition of water and vegetable fat.
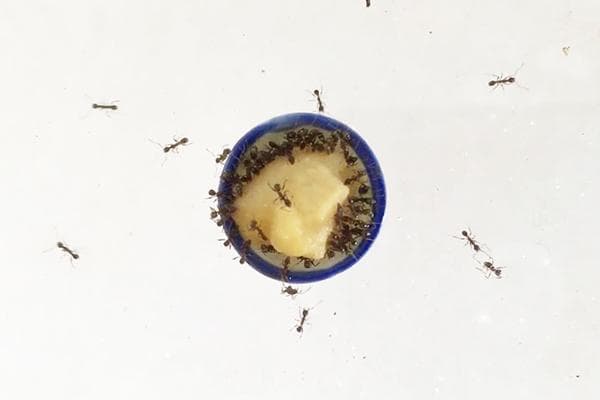
Anthill test
Scientists have conducted this experiment more than once. Ants bypass vegetable fats, and eat natural dairy products in the blink of an eye.
Try to find a family of ants and place a small oil crumb nearby.
Color, taste and smell
If you regularly eat only natural oil, it will not be difficult to distinguish counterfeit oil. The creamy product is characterized by:
- light yellowish color;
- pleasant milky smell;
- subdued creamy taste and melt on the tongue.
Vegetable fat-based oils typically have a deeper yellow color. Sometimes unnaturally white varieties are also found. Having tried a piece of counterfeit in its pure form, you are unlikely to want to eat another one. It will leave a viscosity and an unpleasant taste in your mouth.
Butter is the most frequently counterfeit product in the world. That's why it's so important to check its quality. By conducting a series of home tests, you can easily identify the counterfeit. This means you will protect yourself and your loved ones from health problems.
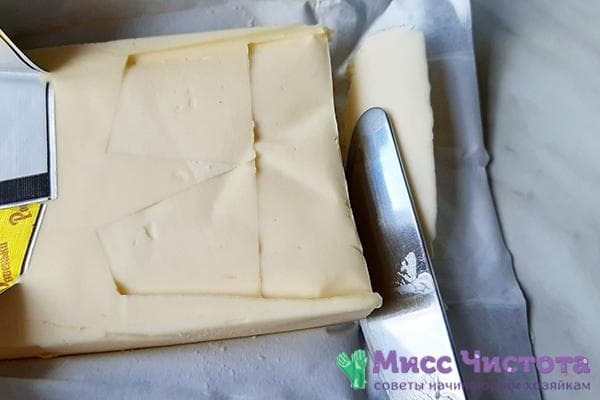






Manufacturers have learned to cleverly deceive customers. Recently in Auchan (Kaluga) I saw Burenkin Meadow oil.The cow is drawn, the fat content is indicated as 82.5 and the price tag says BZMZH. The deception was revealed at home. Using a magnifying glass, I read the composition: it was vegetable oil, mostly consisting of vegetable fats. I returned the oil to the store.
.