How to check the authenticity of a diamond: 5 tests that a real stone will pass
Content:
Diamond is the most coveted stone in the world. A good cut 1 carat costs about $20,000, while a fine cut can be purchased for $75. The most annoying thing is that both options can look stunningly beautiful and expensive. Sometimes it takes a lot of work to distinguish a diamond from a fake. Especially at home. But such experiments are always interesting, and they will help you learn something. Next, we will talk about 5 interesting tests that you can conduct yourself.
A diamond is not a stone for you: what minerals pass off as a cut diamond?
Diamond is the strongest gem. It cannot be scratched even with great force. It can cut glass. Any master knows what diamond coating is. But not everyone is a diamond.

Diamonds are already processed (polished and faceted) diamonds. Only 25% of diamonds are suitable for the jewelry industry.
The cutting of the stone is designed to show all its natural beauty, which is expressed in the extreme play of light. It is thanks to her that the diamond glows from the inside. The spectacle is fascinating. It's a rare person who will refuse diamond jewelry. Women dream of such a gift, men spend fabulous money... There are so many people who want it that no natural reserves would be enough.
That's why diamonds are grown artificially. To make them more accessible, cubic zirconia and some other minerals are cut into diamonds. People are happy to buy them. But there is also another side to the coin. Sometimes cheap stones are passed off as real.
cubic zirconia
Often ordinary cubic zirconias are passed off as cut diamonds. Cubic zirconia is an artificially produced mineral, crystals of zirconium dioxide. It is curious that it was not created for jewelry at all.
The first cubic zirconia was grown in the USSR about 50 years ago. It was intended for use in lasers.
But very soon jewelers noticed the stone. Cubic zirconia has a diamond luster. Its refractive index is 2.15–2.25, which is very close to gemstones. At the same time, the price for it is more than affordable.
In the 90s, cubic zirconias were often passed off as diamonds. Today it is much more difficult to deceive buyers. Their hardness is only 7.5–8.5 on the Mohs scale, while the diamond index is 10. Cubic zirconias are scratched, often have microscopic chips, and become dull from chemicals. They are heavier than diamonds. And any tester can distinguish cubic zirconia right away.
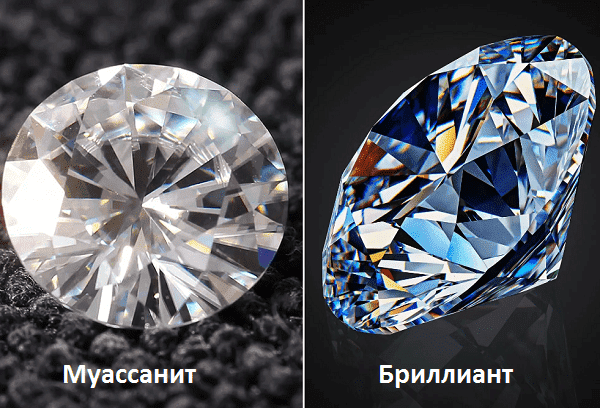
Moissanite
Moissanite is a natural mineral, silicon carbide. It is considered the most expensive diamond substitute. In terms of its optical properties, it even surpasses the original - it plays 2.5 times stronger in the light. The mineral is rare, and its size does not exceed 2 mm.
Few people know that it is not natural moissanite that is inserted into jewelry, but its synthetic analogue, carborundum.
The mineral is slightly inferior to diamond in hardness. According to the Mohs scale, its indicator is 9.25. There is another distinctive feature - birefringence. The spike visible through the platform is double. But this is not easy to consider.
Not every gemologist and tester will be able to distinguish moissanite from a real diamond. The tester must be highly sensitive, and the specialist must be experienced.
Both stones have almost the same thermal conductivity, so inexpensive testers are fooled.
Rock crystal (quartz)
Quartz is one of the most common minerals in the earth's crust. Everyone knows such varieties of quartz as amethyst, citrine, aventurine, and rock crystal. It is rock crystal that is sometimes compared to diamonds.
In ancient Greece, it was believed that rock crystal was ice turned into stone. In jewelry, its variety is valued - Marmarosh diamonds. They are very transparent, clean, well formed, and are often inserted into jewelry without cutting.
Rock crystal is similar to diamond in its transparency and purity. But any professional can easily see the difference between them.
Just look at the photo:
Next to a diamond, rock crystal looks cloudy. Its edges are smooth. If you place a stone against printed text, you will be able to distinguish the letters. In addition, when examined through a magnifying glass, clusters of small bubbles can be detected in the crystal.
Rock crystal is rarely passed off as a diamond. This way they can try to deceive only an inexperienced buyer who buys jewelry second-hand.
Glass
Beautiful rhinestones are made from glass. They differ from acrylic rhinestones by the presence of a strong shine and a high refractive index of light.Sparkling in the sun or in the spotlight on clothes, they really resemble precious stones.
The quality of glass rhinestones depends on the lead, barium or zinc content. The most famous Swarovski rhinestones contain 32% lead oxide. The effect of the play of light is simply amazing. However, glass rhinestones are easily scratched. And they are simply not inserted into jewelry.
Glass is not used in jewelry.
Famous Swarovski rings and earrings contain cubic zirconia. They are the ones most often popularly called “glass”.
What does a diamond look like?
Amazing. As already mentioned, the stone fascinates with the play of light. There are 57 facets in a diamond cut, and this is no coincidence. At the beginning of the 20th century, using calculations that took into account the characteristics of the diamond, ideal cut proportions were derived to achieve maximum radiance.
What does the diamond look like in the photo:
Video:
With all of the above, “fakes” often look brighter than the “original”. Here it is appropriate to recall the expression: “Artificial stones are boring with their shine, but natural stones only sometimes delight you.”
Artificial
In terms of its composition and properties, an artificial diamond is the same as a real one. And even more perfect in some ways. The process of “growing” synthetic diamonds is simple. In laboratory conditions it is obtained in a few hours. Chemists joke: “If you press hard on coal, you get a diamond.” For production, HPHT technology is mainly used, which translates as “high pressure, high temperature”.
Synthetic stone is distinguished by the absence of inclusions. It is homogeneous and perfectly clean. It is extremely difficult to distinguish it from an equally pure real diamond. This can only be done using laboratory tests.
Real
The most significant difference between a natural diamond and an artificial one is the presence of inclusions. In nature, perfectly clean stones are extremely rare. In 99.9% of cases, the thickness contains inclusions of other materials. By the way, it is impossible to see them with the naked eye. It is necessary to examine the stone at multiple magnifications and from different angles.
Interesting to know. Inclusions in a diamond can tell experts where it is located.
Professional authentication methods
Not every jeweler undertakes to check a cut diamond for authenticity. In pawn shops, diamond jewelry is valued without the stone. This is because recognizing a quality craft is very difficult. There is a high probability of making a mistake.
Gemologists are considered specialists in this field. Professional stone analysis includes:
- Inspection through a magnifying glass. First of all, the specialist looks for information at the bottom of the stone. Real jewelry has a mark. CZ is cubic zirconia, and LG and Gemesis created artificial diamonds. Under a magnifying glass they also check the clarity of the edges, the presence of defects, chips, inclusions and other things.
- Play of light. A diamond does not emit a rainbow glow. Its glow is even and silvery in color.
- Weighing on sensitive scales. At the same size, cubic zirconias are heavier than real diamonds.
- Inspection under ultraviolet light and cathode rays. It can provide information about the nature of the origin of the stone and its refining.
- Use of detectors. The devices measure thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, and refractive index. They allow you to quickly and fairly accurately identify cubic zirconias, moissanites and other stones passed off as diamonds.
How to distinguish a diamond from a fake at home?
Anyone can check a diamond for authenticity.To do this, you don’t always need to go to a laboratory or store.
Homemade methods will help you distinguish a natural diamond from a frankly cheap fake.
Start by inspecting the stone:
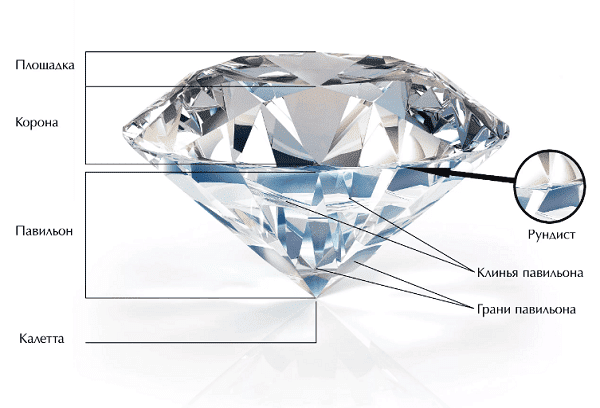
- Pay attention to the girdle. In zirconiums, the side edge is blunt, but in real diamonds it is sharp, like the blade of a sharpened knife. Run your finger along the girdle or look through a magnifying glass.
- Appreciate the sparkle. The diamond sparkles with light, gray-blue flashes. There is a feeling that it glows from within. It flashes with needles. Fake stones sparkle with a stronger surface and with all the colors of the rainbow.
- Defects. Looking at a diamond through a loupe or microscope, you will never find chips on the edges or thread-like inclusions. Small dots may be present.
- Frame. Elite stone is inserted exclusively into precious metals: platinum and gold. Particular attention is paid to the quality of fastenings. A diamond can't dangle. In addition, the distance between the paws is the same. Glue is never used to secure it.
- Price. A real diamond is always an expensive stone, even if it is not of the best quality. In 2021, the average cost of 1 carat is $8,850. The price for decoration is even higher. If the ring or earrings were purchased several times cheaper, most likely the diamonds in them are fake.
Advice. If you don't have a magnifying glass, use macro mode to photograph the jewelry. Enlarge the image on the screen and you will be able to see the stone in detail.
Water
There is a popular myth that a diamond “merges with water.” Allegedly, if you put a stone in a transparent glass of water, you can accidentally drink it. In fact, it's just a beautiful fairy tale.
The diamond is clearly visible in the water.
Firstly, its density is much higher than the density of water - 3.47-3.55 g/cm³ versus 0.10 g/cm³. Secondly, water and diamond have significant differences in the refractive index of light. However, a water test may be helpful.
In a glass of water you can see a doublet - a stone glued together from two different materials.
Vegetable oil
You can identify a diamond at home using a drop of vegetable oil. You can use any: sunflower, olive, flaxseed. The main thing is that the oil is liquid. The test is carried out as follows:
- Oil is applied to the largest edge. If the stone is real, the drop will remain intact; if it is fake, it will break up into many small droplets.
- Place the ring on its side and apply it to the glass. A drop of oil should “glue” the diamond for a few seconds. If the stone does not stick at all, it is most likely fake.
Breath
They say that if you breathe on a real diamond, it will not fog up and will remain just as shiny. This is true.
If condensation forms on a diamond, it evaporates instantly. This is the peculiarity of the surface - it does not retain moisture on itself. Other materials fog up more and retain droplets of moisture longer.
The breathing method is good. But there's one catch. If the diamond is 0.5 carats or less, then its surface is so small, then it will be extremely difficult to see the condensation.
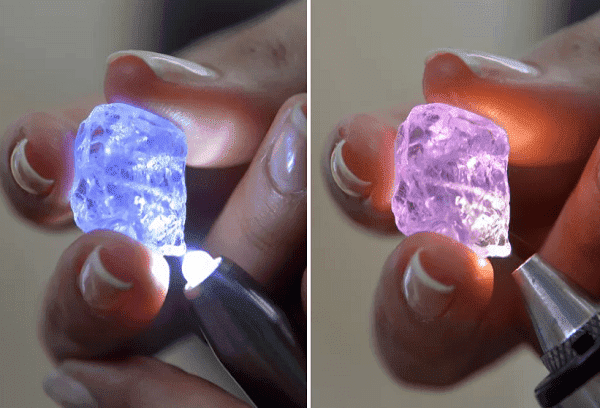
UV light
To test a diamond for authenticity, you can use a UV pen, lighter, or flashlight. You need to turn off the light and shine it on the stone for 1 minute.
Most natural stones emit a blue or bluish glow under UV light.
In addition, they continue to glow for some time in the dark (they have luminescence).But if the stone does not glow, this is not a reason to be upset. Ultraviolet neutral diamonds are found in nature. In Europe they are even valued higher (in the USA it’s the other way around). It is believed that inertness to UV radiation is due to the absence of defects at the molecular level.
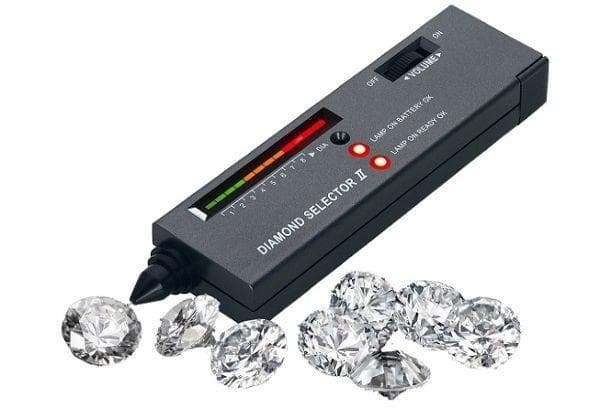
Tester
Diamond authenticity detectors are freely sold on the Internet. They come in different sensitivities. But even the simplest one can easily distinguish cubic zirconia. But to detect mussanite, you need a more expensive device. He evaluates the stone based on its electrical conductivity. Moissanite conducts electricity, but diamond does not.
The tester is brought to the stone at an angle of 90 degrees. Within a few seconds, the result is displayed on the scoreboard. The simplest Diamond Selector II can be bought on Aliexpress for 600 rubles.
Prohibited Methods
One of the most famous tests is glass cutting. A real diamond can cut it, or at least leave scratches. It scratches other stones with the same ease.
We advise you not to resort to barbaric checks. If the stone turns out to be genuine, then you will not spoil it, but you may damage the frame.
Prohibited methods include the following:
- Scratching with a diamond file.
- Glass cutting.
- Heating to high temperatures.
- Hit with a hammer.
Diamond is the hardest stone. And it is true. But at the same time it is also fragile. A blow with a hammer will destroy it.
Authentication check in a laboratory or specialist
You can find out with a 100% guarantee whether a diamond is genuine or fake, only by submitting the stone for examination to a gemological laboratory.
There are such laboratories in all major cities. The most famous in Russia is the Gemological Center of Moscow State University. On average, the examination costs 1,200 rubles. Duration: from 1 hour to 2 days.A written expert opinion and a legal document (certificate) costs a little more - 1500-3000 rubles. Here you can evaluate the stone and find out its real value.
For identification, laboratories use special equipment:
- gemological triplet magnifying glass;
- visible spectrometers with near-UV and IR capabilities;
- Raman spectrometers for analyzing the composition of inclusions, various structural features and impurity centers;
- other.
Even HPHT treated diamonds can be identified in laboratories. They have characteristic crystal lattice defects. When determining the authenticity of a stone, a specialist gives a full conclusion, including checking its quality characteristics.
What affects the price of a diamond?
Diamond is different from diamond. Even “originals” of the same size can differ in price by more than 60%. The most valuable are considered to be untreated, large stones with ideal purity, hardness, color, transparency and cut.
Most gemological laboratories around the world rely on the GIA classification called the “4Cs” to determine the value of diamonds. It was developed in 1953 at the Gemological Institute of America. The higher the 4C score, the more expensive the stone is considered.
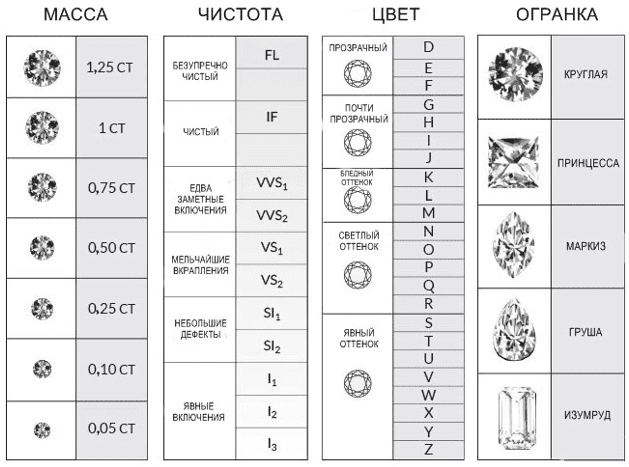
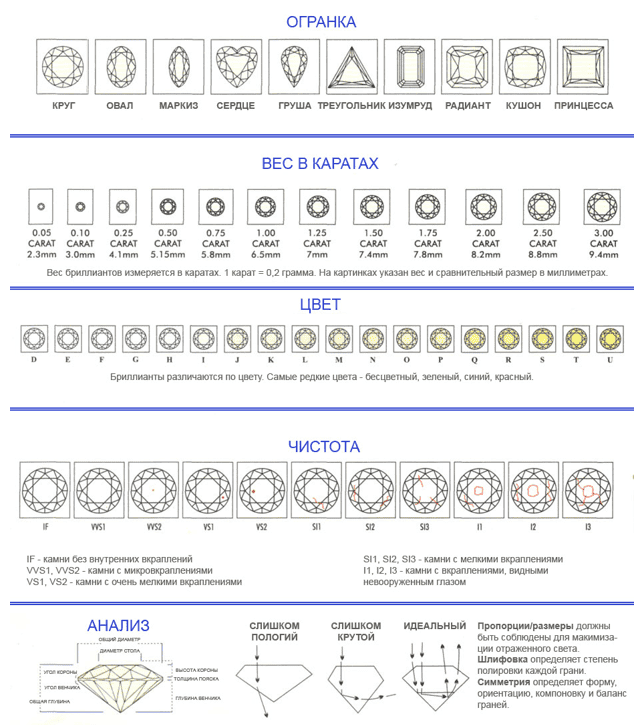
The four main characteristics that determine the quality and cost of diamonds are carat, cut, color, clarity.
- Weight (Carat). 1 carat is equal to 0.2 g. Diamonds larger than 1 carat are considered large. The average weight is 0.3-0.99 carats. Stones smaller than 0.29 carats are considered small.
- Color. The most expensive diamonds are considered to be completely colorless diamonds, which are rare in nature. They belong to group D.There are also stones of a pale yellow hue, fancy colors.
- Clarity. The main evaluation criterion. The fewer inclusions in a stone, the more transparent it is, the higher its cost.
- Quality of cut (Cut). Thanks to skillful cutting, a diamond becomes a diamond. In the expensive version, precise geometry, proportions, and correct angles are observed.
Criteria that will help you roughly evaluate a diamond and determine its quality:
- Table No. 1:
- Table No. 2:
Questions on the topic
How are diamonds counterfeited?
Most often, cubic zirconias and moissanites with a Kr-57 cut are passed off as diamonds. In recent years, so-called “Chinese diamonds” made from diamond dust have appeared on the market. Synthetic diamonds and doublet stones with cheap material glued to the bottom are passed off as natural diamonds. Low-quality diamonds are refined - excess carbon is removed with a laser, after which the stone is passed off as first-class. There are a large number of options for fakes, made with such skill that not every specialist can identify them.
Is it possible to check the stone in a store?
Not only is it possible, but it is also necessary. Buying a diamond ring is not a situation where you can rely on trust. The first thing the store should have is the appropriate certificates issued by a specialized gemological laboratory. Also, at your request, the diamond must be checked by a tester. Such devices are available in all major stores (you should not buy a diamond in others).
Let's summarize. At home, it is impossible for an ordinary person to distinguish a diamond from a fake with 100% certainty. Especially if high-quality moissanite is inserted into the ring, and the stone itself is small. Even a jeweler can make a mistake here.Modern jewelry manufacturing technologies have made great strides forward. Diamonds are counterfeited with very high quality. The only reliable way to find out whether the stone in front of you is real or not is to test it in a laboratory.